UNGM NO: 613759 | NCAGE NO: SGGU2 | DUNS TRACKING ID NO: 2188825 | SIC CODE: 7389















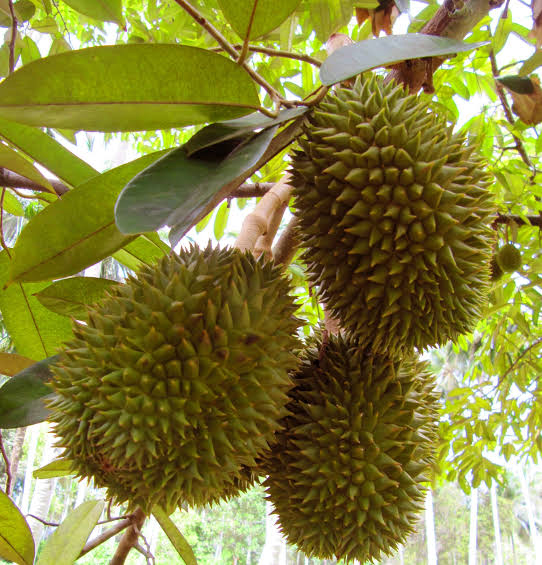
Durians are the most famous of Malaysian fruits due to their powerful aroma, distinctive taste and custardy texture. The famous 19th century naturalist, Alfred Russel Wallace said ‘to eat durian is a new sensation worth a voyage to the East to experience’.
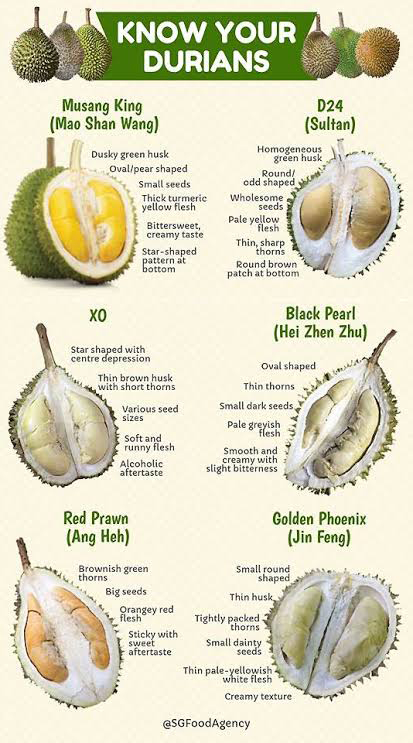
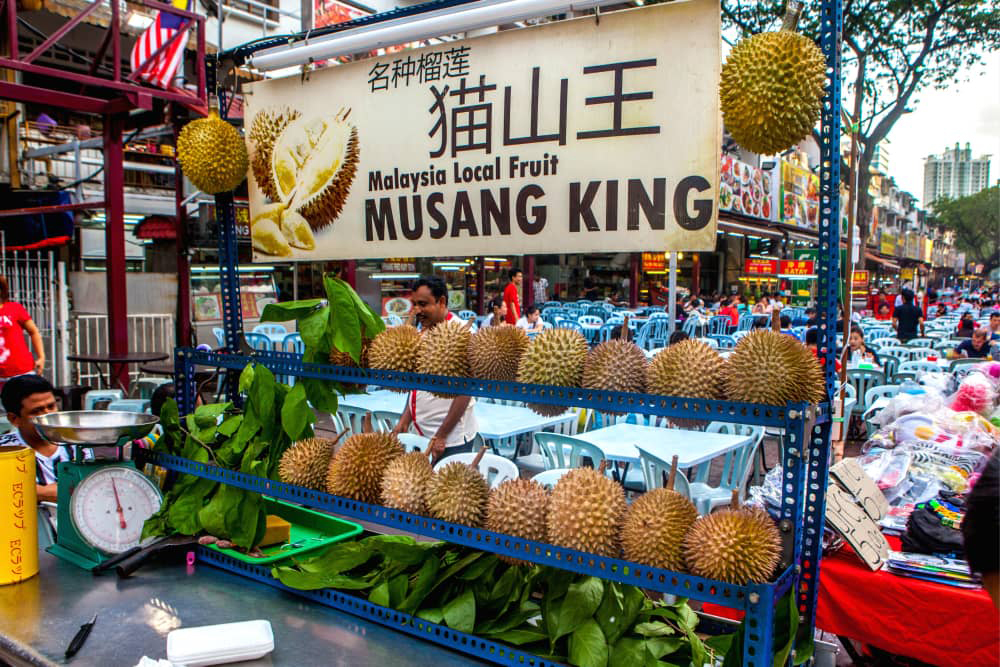
 The most sought after variety is the Musang King, with a creamy texture, smaller seeds (therefore more flesh) and a slightly bitter, fermented aftertaste. Durians in Malaysia are harvested by collecting them from the ground after they have fallen from the tree. Watchmen or boys are often stationed in small palm thatch shelters to keep an eye on their valuable crop.
The most sought after variety is the Musang King, with a creamy texture, smaller seeds (therefore more flesh) and a slightly bitter, fermented aftertaste. Durians in Malaysia are harvested by collecting them from the ground after they have fallen from the tree. Watchmen or boys are often stationed in small palm thatch shelters to keep an eye on their valuable crop.
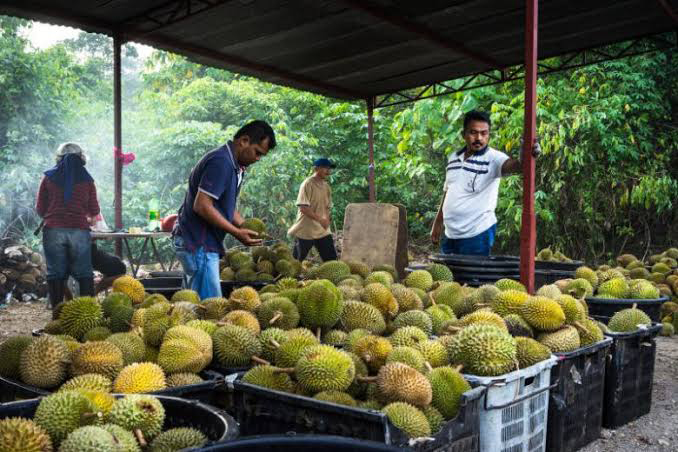
Malaysia grows about 300,000 tonnes of durian every year, with most of it consumed domestically. Total exports in 2018 were 23,381 tonnes, worth RM118.2 million (US$29.4 million), according to Malaysia’s Department of Statistics. A total of 20,793 tonnes or 88.9% of this went to Singapore. And only 236 tonnes were exported to China in the form of pulp and paste.
Following the inking of the new protocol, Malaysia’s first exports of frozen whole fruit durians occurred on 17 June, with five companies approved to export the fruits to China, said Salahuddin Ayub, the minister for agriculture and agro-based industry, in a statement announcing the exports.
Last year, Malaysia’s durian output increased by 61.9% to 341,000 tonnes from 211,000 tonnes in 2017 and is expected to increase in the following years, particularly premium varieties such as the Musang King and Black Thorn.
UKAA’s commercial partners are currently in negotiations with Malaysia to source the best areas across Africa to grow Durian. The ideal conditions to grow Durian, as the Durian experts have reasons to believe, are certain areas in Africa which have the perfect climate to grow this magnificent fruit. The end goal is for Africa to become a competitive exporter of this increasingly popular fruit.
The potential revenue that can be generated and the job creation prospects are enormous, as are the benefits to Kingdom communities and countries that will have the ability to grow this incredible product.
Durian is a tropical fruit distinguished by its large size and spiky, hard outer shell. It has a smelly, custard-like flesh with large seeds. There are several varieties, but the most common one is Durio zibethinus. The fruit's flesh can range in colour. It's most commonly yellow or white but can also be red or green.
Durian grows in tropical regions around the world, particularly in the Southeast Asian countries of Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand. The fruit can grow up to 1 foot (30 cm) long and 6 inches (15 cm) wide. A typical durian fruit has about 2 cups (486 grams) of edible pulp.
Durian is used in sweet and savoury dishes. Both the creamy flesh and seeds are edible, though the seeds need to be cooked.The flavour is described as tasting like cheese, almonds, garlic, and caramel all at once.
Common food preparations of durian fruit include: • juice • seeds, boiled or roasted • soup • candy, ice cream, and other desserts • side dish
 It’s also used in traditional medicine and has some medicinal properties that are currently being studied. One of the most nutritious fruits Durian is very high in nutrients compared to most other fruits.
It’s also used in traditional medicine and has some medicinal properties that are currently being studied. One of the most nutritious fruits Durian is very high in nutrients compared to most other fruits.
One cup (243 grams) of pulp provides (1): • Calories: 357 • Fat: 13 grams • Carbs: 66 grams • Fiber: 9 grams • Protein: 4 grams • Vitamin C: 80% of the Daily Value (DV) • Thiamine: 61% of the DV • Manganese: 39% of the DV • Vitamin B6: 38% of the DV • Potassium: 30% of the DV • Riboflavin: 29% of the DV • Copper: 25% of the DV • Folate: 22% of the DV • Magnesium: 18% of the DV • Niacin: 13% of the DV
This nutrient profile makes durian one of the most nutritious fruits worldwide. It’s also rich in healthy plant compounds, including anthocyanins, carotenoids, polyphenols, and flavonoids. Many of these function as antioxidants (2Trusted Source).
All parts of the durian plant — leaves, husk, roots, and fruit — have been used in traditional Malaysian medicine to treat various illnesses, including high fever, jaundice, and skin conditions (2Trusted Source). Studies suggest that durian fruit offers the following health benefits (2Trusted Source, 3Trusted Source): • Reduces cancer risk. Its antioxidants may neutralize cancer-promoting free radicals. In one test-tube study, durian extract prevented a strain of breast cancer cells from spreading. • Prevents heart disease. Several compounds in durian may help reduce cholesterol levels and your risk of atherosclerosis, or the hardening of your arteries. • Fights infection. The rind contains compounds that have antibacterial and anti-yeast properties. • Lowers blood sugar. Durian has a lower glycemic index (GI) than many other tropical fruits, meaning it may spike blood sugar levels less.
While these studies show promise, many have been done on animals or in test tubes. No solid claims can be made until the health benefits of durian have been confirmed by controlled studies in people.
 Opening a durian's hard, spiky shell often requires gloves or mitts to protect your hands. You need to cut the shell with a knife and pry it open with your hands before gently removing the durian flesh. You can then eat it fresh on its own, paired with sticky rice, or as an ingredient in various dishes.
Opening a durian's hard, spiky shell often requires gloves or mitts to protect your hands. You need to cut the shell with a knife and pry it open with your hands before gently removing the durian flesh. You can then eat it fresh on its own, paired with sticky rice, or as an ingredient in various dishes.
You can find tutorials on how to open a durian fruit, as well as many recipes, online. The flesh is also sold frozen, which slightly changes its texture, making it looser and more stringy.
Durian is also used in prepared foods, such as candy. Yet, while this may give you a sample of its flavour, it won't provide you with the health benefits.
Opinions are mixed about durian's smell. Some people love it, while others hate it. The smell is very strong and has been described as a combination of sulfur, sewage, fruit, honey, and roasted and rotting onions. A study on the aromatic compounds in durian found 44 active compounds, including some that contribute to scents of skunk, caramel, rotten egg, fruit, and soup seasoning (4Trusted Source).
The fruit's smell is so potent that it's banned in many hotels and public transport systems in Southeast Asia. Your impression of the fruit depends on whether you smell the sweet-smelling or stinky compounds more strongly.